Incident Publication
Homestead Complex and Lane 1 Fire Daily Update 09 26 2024
Related Incident: Lane 1 Fire
Publication Type: News
Email: 2024.homesteadcomplex@firenet.gov
Fire Information Line: 541-208-7100 (Staffed 8 a.m. to 8 p.m.)
Facebook: https://t.ly/mSLvP
Inciweb: https://t.ly/syeHa
September 26, 2024
There are five fires under active management within the Lane 1 and Homestead Complex, totaling approximately 35,860 acres, with 623 people assigned. The Lane 1 fire is 99% contained, and the Homestead Complex is 35% contained.
Firefighters are improving containment lines across the fire area by reducing fuels through mastication, chipping wood, and hauling fuels to landings away from the fire. There are still many miles of uncontained fire edge. Crews have been systematically searching fire perimeters and extinguishing all detected hot spots, with mop up and patrol as needed.
Crews are clearing and repairing roads impacted by the fires and by fire suppression activities. 101 miles of roadside have been chipped with 27 miles remaining, and 70 miles of road have been repaired with 58 miles remaining. For the Lane 1 Fire, 80 miles of roadside have been chipped with 5 miles remaining, and 58 miles of road has been repaired with 35 miles remaining.
Rain fell over the fire area yesterday, in amounts ranging from two tenths of an inch in the north to a trace in the south. This rain and cooler weather have reduced fire behavior, and the effects will last for several days. Warmer, drier weather is expected for the next few days, which will dry out fuels and return the potential for fire spread.
On the Horse Heaven Fire, Containment is progressing well on the north end. Crews are patrolling in the south. Chipping and grading continue on the 3839 Road to the east of the fire area. Work on the 010 Road is nearly complete.
The Fuller Lake Fire will continue to back, creep, and smolder in the Boulder Creek Wilderness area. Fuel break work continues in the southeast portion with 4 masticators, 2 crews, and 2 chippers.
On the northern part of the Bullpup Fire, crews are chipping, repairing roads and cleaning culverts. Grading is underway on the 3850 Road which is a major access road for fire crews.
On the No Man Fire, no heat has been detected. Crews will maintain patrols.
On the Lane 1 Fire, Chipping is completed on the east side of the Lane 1 Fire along Pudding Road, and the Umpqua Forest Road Crew has begun road rehabilitation work which is expected to take about a week. Chipping has been completed on the 2241. The rest of Lane 1 is in patrol status.
Closures and fire restrictions: The Umpqua National Forest and the Bureau of Land Management (BLM) have issued revised closure orders. Two closure orders impact the Umpqua National Forest https://t.ly/Mvn6G. A Bureau of Land Management (BLM) Roseburg District closure order is in effect for BLM road(s) 24-1-25 and 24-1-25.1, from the junction with BLM road 24-1-26 (Francis Creek) East to the Roseburg District Boundary in Township 24 South, Range 1, West Section 25. This area will remain closed. https://t.ly/uWX6l. A BLM Northwest Oregon District closure west of the Lane 1 fire has been lifted. https://t.ly/oW1lG.
Weather and fire behavior: Following the passage of yesterday’s cold front and rain, weather will settle into a more seasonable pattern with mostly sunny skies, temperatures ranging from the 60s to 70s, and lower humidity.
Middle Fork Complex Daily Update Sept 26 2024 09 26 2024
Related Incident:
Publication Type: News
**Middle Fork Complex Daily Update Sept. 26, 2024 09-26-2024**
Middle Fork Complex: 61,484 acres, 90% comple on, 526 Personnel
Snag Fire: 33,436 acres, 90% comple on, 162 Personnel
Goat Fire: 26,513 acres, 43% comple on, 67 personnel
Today is expected to be slightly cooler with temperatures in the low 70’s to low 80’s with rela ve humidity falling into the upper teens to upper 20’s. Good rela ve humidity recovery overnight will limit fire behavior. Temperatures expected to heat back up later in the week. No chances of precipita on or thunderstorms are expected in the extended forecast.
Middle Fork Complex – Repair work is wrapping up on the Forest Service 555 road. The Deadwood fire suppression activites are all in repair mode. Scott Lookout continues to see heat to the south, due to increased temperatures causing the lower elevation finer fuels to dry out. Smoke in this area is likely due to this continued weather trend. The clear skies and warmer temperatures will continue to dry the finer fuels throughout the week. Crews are con nuing to monitor these areas for any interior heat.
Goat- Hot Shot crews continue to be in patrol and repair mode, repairing dozer and handline east of the Horse Thief Reservoir. Looking for heat in that area and con nue direct line while mopping up 50 along fires edge, thus preventing fire progression to the west and protecting the values at risk. Containment and comple on line will continue to show more progress.
Snag – 90 percent is completed and repair of firelines are in progress. Crews and engines are still present monitoring and evaluating any concerns. Crews are working on the indirect and direct hand and dozer lines. Suppression repair has been completed around the western, northern, and eastern sides. Crews were able to complete line in the Warm Lake corridor, securing it to Warm Lake Road.
Middle Fork Complex - Suppression Repair= 31 miles of handline completed. 27 miles of dozer line completed.
Goat and Snag Fires - Suppression Repair = 17.1 miles of handline completed. 29.9 miles of dozer line completed.
Firefighters continue work both fire suppression and suppression repair as needed so heavy firefigh ng equipment is moving from site to site. Please use extreme caution while traveling, especially when approaching vehicles, and at intersections.
Closure Orders: https://www.fs.usda.gov/alerts/boise/alerts-notices. Hunters are not allowed access to closed areas. We ask the public to adhere to the closures as they currently exist; in particular, Trail Creek Hot Springs is currently within the closure area for the West Mountain Complex and is closed.
Fire Restrictions: Stage 1 Fire Restrictions have been rescinded for the Boise National Forest. For more information on the restrictions visit https://www.fs.usda.gov/alerts/boise/alerts-notices.
Middle Fork Fire Information: 208-992-3045 (8 a.m. – 8 p.m.)
Email: 2024.middleforkcomplex@firenet.gov
Inciweb: https://inciweb.wildfire.gov/incident-information/idbof-middle-fork-complex-fire-bulldog-and-nellie
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/people/Middle-Fork-Complex-Fire-Boise-National-Forest/61565022204468
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/@2024.middleforkcomplex
BAER INFORMATION BRIEF Preparing for Rain After California Wildfires 09 26 2024
Related Incident: Southern California Post-Fire BAER 2024
Publication Type: News
BAER INFORMATION BRIEF: Preparing for Rain After California Wildfires
Preparing for Rain After California Wildfires
POST-FIRE WATERSHED CONDITIONS—KEY MESSAGES
While many wildfires cause minimal damage to the land and pose few threats to the land or people downstream, some fires cause damage that requires special efforts to prevent problems afterwards.
Summer monsoon thunderstorms and winter rain events in California mountain areas can result in high water runoff and flooding.
Wildfire increases the potential for flooding, post-fire soil erosion and debris flows that could impact campgrounds, fishing areas, homes, structures, roads, and other infrastructure within, adjacent to, and downstream from the burned areas.
Post-fire, watershed conditions will naturally receive and transport water and sediment differently than during pre-fire conditions.
The public and communities adjacent to and downstream from the wildfire areas should expect increased flooding and debris transport during less than average rain events.
SAFETY CONCERNS CONTINUE AFTER THE FIRE IS OUT
The potential for increased water runoff and debris flows are not just a one-year concern.
We recognize the threat potential of flash floods and debris flows may exist for the next several years, depending on the intensity of these storms.
For life and safety concerns, burned area public land closures are sometimes implemented prior to forecast rain events until the burned area fully recovers.
Residents and visitors should remain alert to weather events and plan ahead when travelling along roads within and downstream from the burned areas.
ASSESSING BURNED WATERSHEDS RESPONSE
Forest Service Burned Area Emergency Response (BAER) teams work with each of the national forests, to assess the condition of the watersheds on National Forest System (NFS) lands burned by wildfires.
BAER assessment teams identify potential emergency threats to BAER critical values that may be considered at-risk on federal lands such as:
- Human life and safety.
- NFS property, such as buildings, water systems and infrastructure, utility systems, road and trail prisms.
- Critical natural resources such as water, soil productivity and hydrologic function, areas where invasive species or noxious weeds may impact native or naturalized communities and may include critical habitat or suitable occupied habitat for federally listed threatened or endangered species.
- Critical cultural and heritage resources such as pre-historic and historic properties and sites.
BAER assessment teams recommend emergency stabilization response actions that are implemented on federal land to reduce potential post-fire threats.
PREPARING FOR POTENTIAL FLOODING AND DEBRIS-FLOWS FROM WILDFIRE BURNED AREAS
For values and resources potentially impacted off federal lands, one of the most effective BAER strategies is interagency coordination with local cooperators who assist affected businesses, homes, and landowners with preparing for rain events.
While multi-agency efforts are being taken to reduce the risks to life and safety adjacent to and downstream from the burned areas, nearby residents should develop individual plans to protect themselves and their property.
The USDA Forest Service and the USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS) work together and coordinate with other federal, state and local agencies, and counties that assist private landowners in preparing for increased water run-off and potential flooding impacts.
NRCS and local sponsors prepare damage survey reports for eligible sites on private lands adjacent to and downstream from affected areas. NRCS uses these reports, along with the Forest Service BAER team’s assessment report, to develop emergency measures to reduce the impacts from potential increased water and debris flows, and assist local sponsors to implement recommended emergency measures through its Emergency Watershed Protection (EWP) Program: (NRCS_EWPP_Fact Sheet-2021.pdf (usda.gov)).
All EWP Program–Recovery projects begin with a local sponsor or legal subdivision of state or tribal government. Eligible sponsors include cities, counties, towns, conservation districts, or any federally recognized Native American tribe or tribal organization. Interested public and private landowners can apply for EWP Program–Recovery assistance through one of those sponsors. For more information on NRCS Disaster Assistance Programs: Emergency Watershed Protection | Natural Resources Conservation Service (usda.gov).
The following links provide information and references for state and local county offices of emergency management promote preparedness through its emergency services programs to assist the public to prepare for, respond appropriately to, and quickly recover from natural emergencies that may impact county residents and visitors:
Flood After Fire--California Toolkit
After the Fire—California Resources
California Current Road Conditions
Cal-Fire—Fire and Resource Assistance
California Governor's Office of Emergency Services
California Watershed Emergency Response Team (WERT)
Homes or businesses that could be impacted by flooding from federal land that resulted from wildfires may be eligible for flood insurance coverage from the National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP). Information about NFIP is available through FEMA at www.fema.gov/national-flood-insurance-program, or FEMA Wildfire Increases Flood Risk. Other flood preparedness information is available at www.ready.gov/floods and www.floodsmart.gov/.
LINKS TO ADDITIONAL RESOURCES AND WEBSITES
NRCS Wildfire Disaster Recovery
NRCS Post-Fire Disaster Assistance
FEMA Wildfire Increases Flood Risk
FEMA Flood After Fire—Fact Sheet
Recovering from Wildfire-Damage Assessments
Flood Safety Emergency Preparedness
Be Ready & Prepare for Emergencies
NWS Weather Information—Los Angeles CA
NWS Weather Information—Sacramento CA
NWS Post-Wildfire Flash Flood-Debris Flow Guide
NWS Burn Scar Flash Flood & Debris Flow Risks
Red Cross Emergency Preparedness
BAER SAFETY MESSAGE: Everyone near and downstream from the burned areas should remain alert and stay updated on weather conditions that may result in heavy rains and increased water runoff. Flash flooding may occur quickly during heavy rain events--be prepared to act. Current weather and emergency notifications can be found at National Weather Service website: www.weather.gov/lox/.
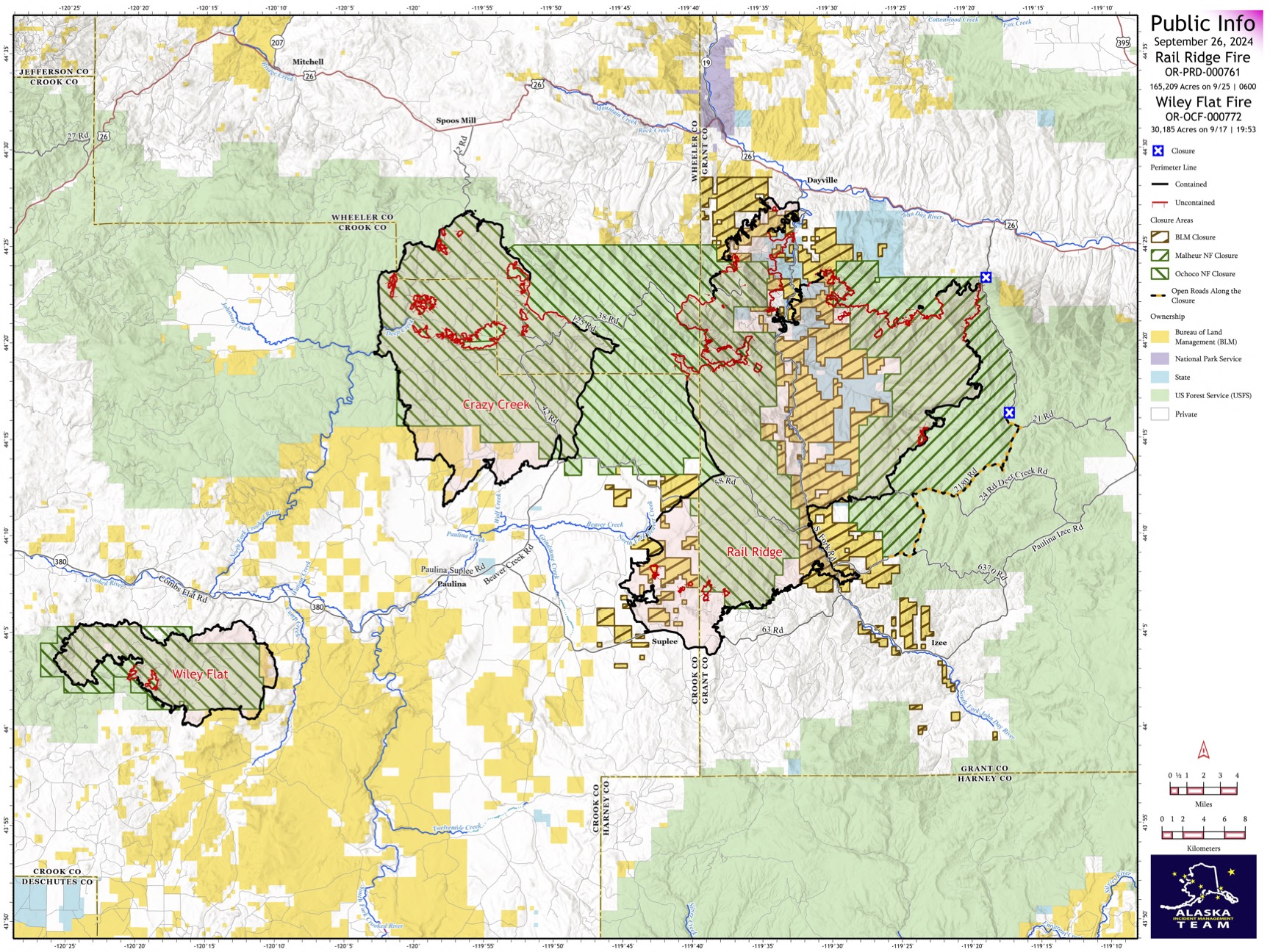
Rail Ridge and Wiley Flat Fire Daily Update 09 26 2024
Related Incident:
Publication Type: News
Rail Ridge and Wiley Flat Daily Update
9-26-24
Rail Ridge Fire
Acres: 165,209 – Containment: 61% – Detection Date: Sept 2, 2024 – Cause: Lightning – Total resources: 1239
Operational Update: Yesterday, a cold frontal passage over the Rail Ridge Fire tested control lines with strong winds, gusting up to 45 MPH. Firefighters were prepared for this forecasted event and utilized aerial resources until around 11AM when winds made it unsafe to fly. Containment lines along Coffee Pot Ridge held, where firefighters will continue to secure and mop up during today’s shift. The fire did progress in the Black Canyon Wilderness, from the south side of Black Canyon Creek and is now established in Honeymoon Basin. An Uncrewed Aerial System (drone) is being utilized today to collect intel and identify areas of heat. Firefighters will continue to focus on increasing containment on the northeast side of the fire. Mop up and suppression repair efforts will continue around the perimeter of the fire where containment has been established.
Wiley Flat Fire
Acres: 30,186 – Containment: 94% – Detection Date: Sept 2, 2024 – Cause: Lightning – Total resources: 59
Operational Update: Yesterday’s weather event confirmed confidence in containment lines on the Wiley Flat Fire. Mop up and suppression repair will continue as crews work to eliminate any remaining heat within the fire perimeter.
Weather
Good relative humidity recoveries occurred over the fires area last night. Cooler temperatures, light winds, and sunny skies are expected today. A dry, warming trend is forecasted over the next few days, as a high-pressure system moves into the region.
Evacuations
Rail Ridge Evacuations: Level 1 and 2 evacuation zones for the Rail Ridge Fire remain in Grant County. Wiley Flat Evacuations: Level 2 and 3 evacuation zones are in place for the Wiley Flat Fire in Crook County. For Current Evacuation Levels in Wheeler, Crook and Grant counties, please visit: https://linktr.ee/RailRidgeFire
Closures
The U.S. Forest Service and Bureau of Land Management have implemented closures for the Rail Ridge and Wiley Flat Fires. For more details and closure maps, visit https://linktr.ee/RailRidgeFire
#RailRidgeFire2024 #WileyFlatFire2024 #FireYear2024
BAER INFORMATION BRIEF Understanding Soil Burn Severity09 26 2024
Related Incident: Southern California Post-Fire BAER 2024
Publication Type: News
BAER INFORMATION BRIEF: Understanding Soil Burn Severity
Understanding Soil Burn Severity
We tend to think of wildfire burn severity in terms of the visual impacts to above-ground vegetation, but the post-fire landscape response (erosion, flooding, and mass movement) is generally more strongly correlated to soil burn severity. When characterizing soil burn severity, looking at the vegetation is a good starting place to understand the conditions on the ground.
Armed with that information, the BAER team’s watershed specialists (soil scientists, hydrologists, and geologists) ground-truth different vegetation burn intensities to tease out patterns of how fire affected and changed the properties of the soil. Pre-fire ground cover, forest type, fire behavior, slope, aspect, and other factors all influence soil burn severity. After field observations are collected, specialists adjust the vegetation severity map to create the soil burn severity (SBS) map. The SBS is broken into four different classes: unburned (green), low severity (blue), moderate severity (yellow), and high severity (red).
So, what do these different classifications mean?
LOW severity areas generally have intact and recognizable litter layers (organic material on the forest floor, such as pine needles and twigs). These litter layers may be charred but are not consumed. Underlying topsoil is intact, and near-surface fine roots are unburned. These soils have enough cover to protect them from erosion during rain events because their natural porosity and structure allow rain to soak into the soil instead of running off, while fine roots provide stability. In low severity areas, burns may have been patchy islands of green vegetation and intact canopies may be present.
MODERATE severity areas generally have more—up to 80% of their pre-fire surface litter layers consumed by fire. Black or gray ash may be present on the soil surface. Fine roots near the surface may be scorched and killed. Topsoil layers are generally intact with minimal impacts to the soil’s ability to absorb moisture. Soils with moderate severity are more susceptible to erosion in post-fire rain events because they have lost protective surface cover and may have less surface stability because of root mortality.
HIGH severity areas generally have had all their pre-fire surface litter layers consumed by fire. White or gray ash may be present on the soil surface. Fine roots are often fully burned/consumed within several inches of the soil surface, and even large tree roots may have burned deep into the soil. Soil may be powdery or grainy and loose, unable to bind together and retain water. These soils are very susceptible to erosion and often have high surface run-off during rainstorms.
So, what does the BAER team do with the SBS map?
The BAER team uses the SBS map to make predictions about how the landscape will respond after fires. Soil scientists consider where soil productivity will be degraded due to erosion losses and where sediment may move into stream channels. Hydrologists use the SBS to predict watershed response—surface runoff from high SBS areas in rainstorms can produce more “flashy” behavior in stream systems. Geologists use the SBS to inform predictions for debris flow or other mass movement potential based on reduced soil stability in steep drainages.
BAER teams focus on emergency responses to stabilize burned areas that may impact Forest Service critical infrastructure or other values located within or immediately downstream of high soil burn severity areas.
BAER SAFETY MESSAGE: Everyone near and downstream from the burned areas should remain alert and stay updated on weather conditions that may result in heavy rains and increased water runoff. Flash flooding may occur quickly during heavy rain events--be prepared to act. Current weather and emergency notifications can be found at National Weather Service website: www.weather.gov/lox/.
Willamette Complex North Fire Update 09 26 2024
Related Incident: North Willamette Complex
Publication Type: News
Willamette Complex North Update
Boulder Creek, Ore, Linton Creek, 374 and Pyramid Fires
Fire Update for Thursday, September 26 through Friday, September 27, 2024
Fire updates will be provided for a two-day operational period.
InciWeb: https://inciweb.wildfire.gov/incident-information/orwif-north-willamette-complex
Willamette Complex North Facebook Page: https://www.facebook.com/profile.php?id=61565845313387
Email:2024.WillametteComplex.North@firenet.gov
Information line: 541-208-1262 Hours: 8 a.m. to 8 p.m.
Overview: The fire areas are experiencing cooler temperatures and an increase in humidity, forecasted for the next few days. Crews were limited in their work Wednesday as .10 to .75 inches of rain fell in the fire areas, bringing with it gusting winds with the potential to bring down fire-weakened trees. Thursday, firefighters are continuing suppression repair work. Fuel moistures will continue to limit fire activity. Little to no fire growth is anticipated within the North Complex over the next few days. Willamette National Forest has rescinded fire restrictions and campfires are once again allowed outside of developed campgrounds and restrictions on chainsaws, off-highway vehicles, and smoking have been lifted. It is still critical to completely extinguish campfires until they are cold to the touch, even with the reduced fire risk.
Boulder Creek: 523 acres, 51% contained
Located 5 miles east of McKenzie Bridge. Fire behavior was minimal yesterday, but firefighters are still locating and addressing hotspots. Mastication has been completed and firefighters will continue to mop up containment lines and fire suppression repair work. Crews are pulling hose and removing excess equipment.
Ore: 3,484 acres, 80% contained
Located 7 miles northeast of Blue River. Ore Fire received about ½” of rain yesterday. Crews are engaged in suppression repair work. Fire activity has remained low.
374: 62 acres, 0% contained and Linton Creek: 1,309 acres, 0% contained
Located in the Three Sisters Wilderness. These fires received rain yesterday and fire activity has remained minimal. Despite the warm weather on Tuesday, these fires have remained in their footprints adjacent to natural barriers and previous fire scars. Both fires will continue to be in a monitoring status, with no additional action needed at this time.
Pyramid: 1,312 Acres, 100% contained
East of Middle Santiam Wilderness. This fire received about ¾” of rain yesterday and remains fully contained with minimal fire behavior and scattered areas of heat in the interior of the fire area. Firefighters are continuing with suppression repairs. Tomorrow, Northern Rockies Incident Management Team 6 will be transitioning this fire back to Willamette National Forest and Type 4 organization.
Willamette National Forest Area Closures: Forest officials are continually evaluating closure orders and will adjust as conditions allow. Fire-related closures remain in place on the McKenzie River Ranger District, as well as on the Middle Fork Ranger District in the immediate fire operations area for public and firefighter safety. Please respect and avoid all closed areas of the national forest.
Source: https://www.fs.usda.gov/detail/willamette/fire/?cid=fseprd552029.
Road Closures: OR-242 remains closed to all traffic between the intersection with OR-126 and the Dee Wright Observatory (mileposts 55 to 75). For current road conditions, please check Oregon Department of Transportation’s website: https://www.tripcheck.com/.
BAER INFORMATION BRIEF Fire Severity and Fire Intensity Effects 09 26 2024
Related Incident: Southern California Post-Fire BAER 2024
Publication Type: News
BAER INFORMATION BRIEF: Fire Severity and Fire Intensity Effects
There are several types of fire severity and intensity maps that you may see. Although they look different for the same fire, they may also all be accurate. This is because fire severity or intensity are different measures of the fire effects on a specific resource such as soils, tree canopies, vegetation or wildlife habitat. Burned Area Emergency Response (BAER) maps are primarily measures of fire effects on soils. The following is a description of BAER fire severity mapping for soil burn severity levels.
SOIL BURN SEVERITY RATING OVERVIEW:
High Soil Burn Severity Rating: (severe damage to the soils): deeply burned soils with high water repellent soils (tend to be places where the fire burned the forest canopy, ground cover, roots, and organic matter in the topsoil).
Moderate Soil Burn Severity Rating: burned soil with moderate water repellent soils (much of the root, soil structure, and organic matter stayed intact and could help buffer the rainstorms that might cause erosion) can produce increased water run-off and soil erosion depending on the timing, magnitude, and duration of future precipitation. The remaining vegetation could quickly re-sprout and provide some cover from dead needles and leaf fall to reduce erosion.
Low Soil Burn Severity Rating: light soil burning includes land that may have burned in recent occurrences with brush or young timber growing on it.
KEY MESSAGES:
• Fire severity and intensity are separate measures of the effects of fire on a defined resource.
• All fire severity or intensity maps view landscapes from different perspectives, so various maps of the same fire can look very different, and all be accurate.
• The BAER soil burn severity maps specifically focus on severity to soils and watersheds.
• There are also several other types of fire severity or intensity maps – many of which focus on different aspects of vegetation such as, Burned Area Reflectance Classification (BARC) and Vegetation severity or intensity maps are both vegetation maps but will also look different for the same location and time.
• Vegetation severity and intensity maps also come from a number of different perspectives, and can be short-term or long-term views.
• During post-fire assessments, the BAER team uses the term “soil burn severity” to differentiate post-fire soil properties from fire effects on vegetation (such as tree mortality), and/or general fire effects on the long-term ecosystem health.
• When a fire slowly consumes fuel (long residence time), the fire (soil burn) severity is usually high.
• Ground cover refers to the organic material on the top of the soil layer, and includes vegetative litter, duff, and woody debris.
• When organic material within the ground cover and within the soil structure burns at high intensity, some of the water repellent components vaporize, and condense on the soil at the surface or deeper depending on the severity of the fire.
• The correlation between fire intensity and soil burn severity is not always direct because the amount of heat generated and time duration both plays a critical role in the fire effects to soil.
• Because of the variability of fuel consumption, soil heating typically is non-uniform across landscapes.
• Wildfire does not always impact soils and vegetation in the same way.
• A hot, fast moving fire can consume much of the vegetation and move through so quickly that the soils remain largely intact.
• Soil scientists evaluate preliminary burn maps from satellite imagery to determine the effects and create a soil burn severity map.
• Hydrologists use that information to model storm runoff over the burned area to estimate potential flood impacts to lives and property.
• Foresters use the same satellite images to create a different map that displays post-fire impacts to the trees.
• A hot, fast-moving fire (wind-driven) can consume the majority of vegetation (especially when dry with low fuel moistures) in a burned area and can be classified as a high intensity fire area by fire ecologists/fire behavior analysts.
• When the duration (also described as residency time) of the fire is short (fast moving, wind-driven), it can result in a low-to-moderate soil burn severity rating by BAER soils scientists because the soil did not get a lot of lingering heat on the ground.
BAER SAFETY MESSAGE: Everyone near and downstream from the burned areas should remain alert and stay updated on weather conditions that may result in heavy rains and increased water runoff. Flash flooding may occur quickly during heavy rain events--be prepared to act. Current weather and emergency notifications can be found at the National Weather Service website: www.weather.gov/lox/.
BAER INFORMATION BRIEF Burned Area Emergency Response BAER Limitations 09 26 2024
Related Incident: Southern California Post-Fire BAER 2024
Publication Type: News
BAER INFORMATION BRIEF: Burned Area Emergency Response (BAER) Limitations
While many wildfires cause minimal damage to the land and pose few threats to the land or people downstream, some fires result in damage that requires special efforts to reduce impacts afterwards. Loss of vegetation exposes soil to erosion; water run-off may increase and cause flooding, soil and rock may move downstream and damage property or fill reservoirs putting community water supplies and endangered species at-risk.
The Burned Area Emergency Response (BAER) program is designed to identify and manage potential risks to resources on National Forest System lands and reduce these threats through appropriate emergency measures to protect human life and safety, property, and critical natural or cultural resources. BAER is an emergency program for stabilization work that involves time-critical activities to be completed before the first damaging storm event to meet program objectives.
BAER Objectives:
- Determine whether imminent post-wildfire threats to human life and safety, property, and critical natural or cultural resources on National Forest System lands exist and take immediate actions, as appropriate, to manage the unacceptable risks.
- If emergency conditions are identified, mitigate significant threats to human life and safety, Forest Service property and other critical natural and cultural resource values.
- Prescribe emergency response actions to stabilize and prevent unacceptable degradation to natural and cultural resources, to minimize threats to life or property resulting from the effects of a fire, or to repair/replace/construct physical improvements necessary to prevent degradation of land or resources.
- Implement emergency response actions to help stabilize soil; control water, sediment and debris movement and potentially reduce threats to the BAER critical values identified above when an analysis shows that planned actions are likely to reduce risks substantially within the first year following containment of the fire.
- Monitor the implementation and effectiveness of emergency treatments that were applied on National Forest System lands.
BAER Interagency Coordination:
Post-fire emergency response is a shared responsibility. There are several Federal, State and local agencies that have emergency response responsibilities or authorities in the post-fire environment. The BAER team coordinates with these agencies to look at the full scope and scale of the situation to reduce the potential threats to human life and property. It is important that BAER efforts are communicated with all affected and interested cooperating agencies and organizations regarding other post-fire recovery and restoration efforts.
BAER treatments cannot prevent all of the potential flooding or soil erosion impacts, especially after a wildfire-changed landscape. It is important for the public to stay informed and prepared for potentially dramatic increased run-off events.
One of the most effective BAER strategies is interagency coordination to provide post-fire threat information to local cooperators who can assist affected businesses, homes, and landowners to prepare for rain events. For example, the Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS) has the Emergency Watershed Protection (EWP) program for post-emergency assistance on private and tribal land, the National Weather Service (NWS) has responsibility for flood warning alerts, the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) has flood insurance and other responsibilities if the area is a Presidentially-declared emergency, Resource Conservation Districts (RCD) and counties, as well as State and local-highway and emergency services departments, Flood Control authorities, etc. It is important that landowners work directly with NRCS and other agencies to determine appropriate actions needed to protect private structures and other assets.
BAER Process:
BAER assessment teams are staffed by specially trained professionals that may include: hydrologists, soil scientists, engineers, biologists, botanists, archeologists, and others who evaluate the burned area and prescribe temporary emergency stabilization actions on National Forest System lands to protect the land quickly and effectively. BAER assessments usually begin before a wildfire has been fully contained.
A BAER assessment team conducts field surveys and uses science-based models to rapidly evaluate and assess the burned area and prescribe emergency stabilization measures. The team generates a “Soil Burn Severity” map by using satellite imagery which is then validated and adjusted by BAER team field surveys to assess watershed conditions and model potential watershed response from the wildfire. The map identifies areas of soil burn severity by categories of very low/unburned, low, moderate, and high which may correspond to a projected increase in watershed response. The higher the burn severity, the less the soil will be able to absorb water when it rains. Without absorption, there will be increased run-off with the potential of flooding.
The BAER team presents these findings in an assessment report that identifies immediate and emergency actions needed to address post-fire risks to human life and safety, property, cultural and critical natural resources. This includes early detection and rapid response (EDRR) treatments to prevent the spread of noxious weeds into native plant communities. The BAER report describes watershed pre- and post-fire watershed response information, areas of concern for life and property, and recommended short-term emergency stabilization measures for Forest Service lands that burned.
In most cases, only a portion of the burned area is actually treated. Severely burned areas steep slopes, and places where water run-off will be excessive and may impact important resources, are focus areas and described in the BAER assessment report if they affect critical values. Response action timing is essential to ensure the emergency stabilization measures are effective.
There are a variety of emergency stabilization actions that the BAER team can recommend for Forest Service land such as mulching with agricultural straw or chipped wood to protect soil productivity, increasing road drainage to keep roads and bridges from washing-out during post-fire floods, and early detection rapid response invasive plant treatments to prevent spread of weeds into native plant communities. BAER treatments are preventative in nature but cannot prevent all damage, especially debris torrents in areas that are prone to sliding and have lost critical root structure from plants.
The Cans and Cannots of BAER:
What BAER Can Do:
- Install water or erosion control devices
- Seed or mulch for erosion control or stability reasons
- Install erosion control measures at critical cultural sites
- Install temporary barriers to protect treated or recovering areas
- Install warning signs
- Replace minor safety related facilities, like burned guard rails
- Install appropriate-sized drainage features on roads, trails
- Remove critical safety hazards
- Prevent permanent loss of T&E habitat
- Monitor BAER treatments
- Implement EDRR treatments to minimize the spread of noxious weeds into native plant communities
What BAER Cannot Do:
- Prevent all flooding and debris flows
- Replant commercial forests or grass for forage
- Excavate and interpret cultural sites
- Replace burned pasture fences
- Install interpretive signs
- Replace burned buildings, bridges, corrals, etc.
- Repair roads damaged by floods after fire
- Remove all hazard trees
- Replace burned habitat
- Monitor fire effects
- Treat pre-existing noxious weeds
BAER Funding:
Special Emergency Wildfire Suppression funds are authorized for BAER activities and the amount of these expenses varies with the severity of the fire season. Some years see little BAER activity while other years are extremely busy.
Because of the emergency nature of BAER, initial requests for funding of proposed BAER treatments are supposed to be submitted by the Forest Supervisor to the Regional Office within 7 days of total containment of the fire. The Regional Forester’s approval authority for individual BAER projects is limited. Approval for BAER projects exceeding this limit is forwarded onto the Washington Office.
BAER SAFETY MESSAGE: Everyone near and downstream from the burned areas should remain alert and stay updated on weather conditions that may result in heavy rains and increased water runoff. Flash flooding may occur quickly during heavy rain events--be prepared to act. Current weather and emergency notifications can be found at the National Weather Service website: www.weather.gov/lox/.
BAER INFORMATION BRIEF Key Elements of a BAER Assessment 09 26 2024
Related Incident: Southern California Post-Fire BAER 2024
Publication Type: News
BAER INFORMATION BRIEF: Key Elements of a BAER Assessment
Forest Service BAER assessment teams are established by Forest Supervisors before wildfires are fully contained. The teams coordinate and work with the USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS), Bureau of Land Management (BLM), Fish & Wildlife Service (FWS), National Weather Service (NWS), local counties, State Department of Transportation, and other federal, state, and local agencies to strategically assess potential post-fire impacts to the watersheds burned from wildland fires.
The BAER assessment teams are evaluating watershed conditions to determine the level of potential risks to human life, safety, property, critical natural and cultural-heritage resources, and determine if there are appropriate and effective emergency stabilization measures that can be implemented on federal lands in a timely manner to reduce unacceptable risks from potential flooding and debris flow threats.
The BAER assessment team conducts field surveys and uses science-based models to rapidly evaluate and assess the burned area.
BAER assessment teams are staffed by specially trained professionals that may include: hydrologists, soil scientists, engineers, geologists, biologists, botanists, archeologists, geographic information system mapping specialists, recreation and trails specialists, and others who evaluate the burned area and prescribe emergency response actions to protect the land quickly and effectively.
BAER assessments usually begin before a wildfire has been fully contained.
The BAER assessment team generates a “Soil Burn Severity” map by using satellite imagery which is then validated and adjusted by BAER team field surveys to assess watershed conditions and watershed response to the wildfire. The map identifies areas of soil burn severity by categories of low/unburned, moderate, and high which corresponds to a projected increase in watershed response.
The BAER team presents these findings and treatment recommendations to the Forest Supervisor in an assessment report that identifies immediate and emergency stabilization actions needed to address potential post-fire risks to human life and safety, property, cultural-heritage and critical natural resources on National Forest System lands.
The BAER report describes watershed pre- and post-fire response information, areas of concern for human life, safety and property, and recommended short-term emergency stabilization actions for federal lands that burned.
In most cases, only a portion of the burned area is actually treated.
If the BAER assessment team determines there may be potential emergency situations, the short-term goal is to have flood and erosion control protection measures completed before the first large, damaging rain events occur.
Timely implementation is critical if BAER emergency response actions are to be effective.
The BAER assessment team coordinates with other federal and local agencies, and counties that assist private landowners in preparing for increased run-off and potential flooding.
Federal assistance to private landowners regarding post-fire potential impacts is the primary responsibility of the NRCS through the Emergency Watershed Protection (EWP) program (www.nrcs.usda.gov/wps/portal/nrcs/main/national/programs/landscape/ewpp/)
NRCS in coordination with additional state, local and federal agencies conduct damage survey reports for the private land adjacent to and downstream from the burned areas. NRCS uses these reports, along with the BAER team’s assessment report, to develop recommended emergency measures for businesses and private home and landowners to reduce the impacts to their property from potential increased water and debris flows.
BAER SAFETY MESSAGE: Everyone near and downstream from the burned areas should remain alert and stay updated on weather conditions that may result in heavy rains and increased water runoff. Flash flooding may occur quickly during heavy rain events--be prepared to act. Current weather and emergency notifications can be found at the National Weather Service website: www.weather.gov/lox/.
BAER INFORMATION BRIEF Forest Service BAER Program Overview 09 26 2024
Related Incident: Southern California Post-Fire BAER 2024
Publication Type: News
BAER INFORMATION BRIEF: Forest Service BAER Program Overview
The Burned Area Emergency Response (BAER) program is designed to identify and manage potential risks to resources on National Forest System lands and reduce these threats through appropriate emergency measures to protect human life and safety, property, and critical natural or cultural resources. BAER is an emergency program for stabilization work that involves time-critical activities to be completed before the first damaging event to meet program objectives:
BAER Objectives:
- Determine whether imminent post-wildfire threats to human life and safety, property, and critical natural or cultural resources on National Forest System lands exist and take immediate actions, as appropriate, to manage the unacceptable risks.
- If emergency conditions are identified, mitigate significant threats to health, safety, human life, property, and critical cultural and natural resources.
- Prescribe emergency response actions to stabilize and prevent unacceptable degradation to natural and cultural resources, to minimize threats to critical values resulting from the effects of a fire, or to repair/replace/construct physical improvements necessary to prevent degradation of land or resources.
- Implement emergency response actions to help stabilize soil; control water, sediment and debris movement and potentially reduce threats to the BAER critical values identified above when an analysis shows that planned actions are likely to reduce risks substantially within the first year following containment of the fire.
- Monitor the implementation and effectiveness of emergency treatments that were applied on National Forest System lands.
While many wildfires cause minimal damage to the land and pose few threats to the land or people downstream, some fires result in damage that requires special efforts to reduce impacts afterwards. Loss of vegetation exposes soil to erosion; water run-off may increase, and cause flooding, soil and rock may move downstream and damage property or fill reservoirs putting community water supplies and endangered species at-risk.
The BAER team presents these findings in an assessment report that identifies immediate and emergency actions needed to address post-fire risks to human life and safety, property, cultural and critical natural resources. This includes early detection and rapid response (EDRR) treatments to prevent the spread of noxious weeds into native plant communities. The BAER report describes watershed pre- and post-fire watershed response information, areas of concern for life and property, and recommended short-term emergency stabilization measures for Forest Service lands that burned.
In most cases, only a portion of the burned area is actually treated. Severely burned areas steep slopes, and places where water run-off will be excessive and may impact important resources, are focus areas and described in the BAER assessment report if they affect critical values. Time is critical if the emergency stabilization measures are to be effective.
A BAER assessment team conducts field surveys and uses science-based models to rapidly evaluate and assess the burned area and prescribe emergency stabilization measures. The team generates a “Soil Burn Severity” map by using satellite imagery which is then validated and adjusted by BAER team field surveys to assess watershed conditions and model potential watershed response from the wildfire. The map identifies areas of soil burn severity by categories of very low/unburned, low, moderate, and high which may correspond to a projected increase in watershed response. The higher the burn severity, the less the soil will be able to absorb water when it rains. Without absorption, there will be increased run-off with the potential of flooding.
BAER Funding:
Special Emergency Wildfire Suppression funds are authorized for BAER activities and the amount of these expenses varies with the severity of the fire season. Some years see little BAER activity while other years are extremely busy.
Because of the emergency nature of BAER, initial requests for funding of proposed BAER treatments are supposed to be submitted by the Forest Supervisor to the Regional Office within 7 days of total containment of the fire. The Regional Forester’s approval authority for individual BAER projects is limited. Approval for BAER projects exceeding this limit is to the Washington Office.
BAER SAFETY MESSAGE: Everyone near and downstream from the burned areas should remain alert and stay updated on weather conditions that may result in heavy rains and increased water runoff. Flash flooding may occur quickly during heavy rain events--be prepared to act. Current weather and emergency notifications can be found at the National Weather Service website: www.weather.gov/lox/.

 InciWeb
InciWeb